Wait Program Intermediate Event
 The Wait Program Intermediate Event element is located in the
Event & Gateway drawer of the process editor palette.
The Wait Program Intermediate Event element is located in the
Event & Gateway drawer of the process editor palette.
Element Details
This element is one of Axon.ivy facilities to integrate custom-made software, legacy systems, proprietary applications or any other external system through an Axon.ivy Java interface. At an Intermediate Event element the process execution is interrupted and waits for an external event to occur. Technically spoken the current task will be ended and a new system task is created that waits for the intermediate event. If the intermediate event is fired the new task and therefore the process after the intermediate event will be executed.
You provide a listener for the external event by implementing a Java
class that implements the
IProcessIntermediateEventBean
interface.
The Wait Program Intermediate Event Element instantiates the Java class
and can then trigger the intermediate event by calling the method
fireProcessIntermediateEventEx on the Axon.ivy runtime engine
IProcessIntermediateEventBeanRuntime.
The common way to implement an
Intermediate Event bean is to extend the abstract base class
AbstractProcessIntermediateEventBean.
The interface also includes an
inner editor class to parametrize the bean. You will find the
documentation of the interface and the abstract class in the Java Doc of
the Axon.ivy Public API.
Note
An Axon.ivy Engine Enterprise Edition consists of multiple engine instances (nodes) that are running on different machines.
Normally process intermediate event beans are instantiated on every node but only started on the master node. This guarantees that for each Intermediate Event process element only one bean is running, no matter what the total number of nodes in the Engine Enterprise Edition is.
However, if you need your intermediate event bean to be started on all cluster nodes, you may instruct the server to do so. Just have your bean class implement the (empty) marker interface IMultiNodeCapable and the above restriction will no longer apply.
Please be aware of the fact that having multiple running instances of the same bean may lead to race conditions.
Inscription
Name Tab
The Name Tab is included in the mask of all process elements and contains the name and a description of the element.
Event Tab
On this tab you define the Java class that the IntermediateEvent should instantiate, the identifier of the event to wait for and the timeout behaviour.
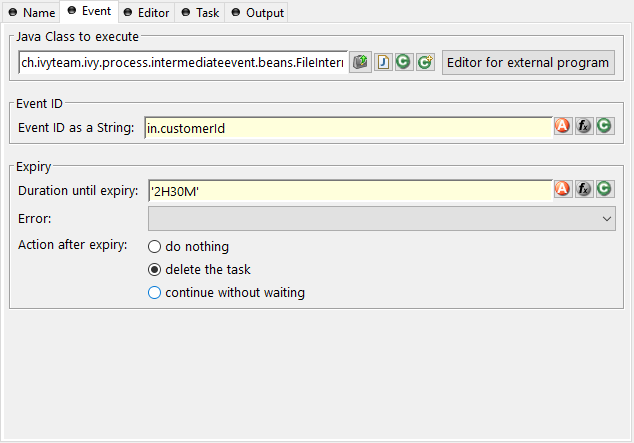
- Java Class to execute
Fully qualified name of the Java class that implements the IProcessIntermediateEventBean interface. Use the New Bean Class Wizard (
 ) to create a new Java
source file with an example implementation of the bean class.
) to create a new Java
source file with an example implementation of the bean class.- Event ID
Because multiple cases (process instances) can wait on the same intermediate event you must specify which event belongs to which waiting case. Here you specify the identifier of the event the current case should wait for.
Warning
The event identifier as a String must be unique. Do not use a static string like
"myID". A good practice is to integrate the case identifier (ivy.case.getIdentifier()) into the event id.- Timeout
Here you can specify a time (Duration) how long the current case should wait for an intermediate event and what should happen if no event has been received after this time. You can optionally start an exception process, delete the waiting task or continue the waiting task without receiving an intermediate event.
Editor Tab
This tab displays the editor that can be integrated in the external Java
bean of the process element. The editor is implemented as an inner
public static class of the Java bean class and must have the name
Editor. Additionally the editor class must implement the
IProcessExtensionConfigurationEditorEx
interface. The common way to
implement the editor class is to extend the abstract base class
AbstractProcessExtensionConfigurationEditor
and to override the
methods createEditorPanelContent, loadUiDataFromConfiguration
and saveUiDataToConfiguration. The method
createEditorPanelContent can be used to build the UI components of
the editor. You can add any AWT/Swing component to the given
editorPanel parameter. With the given editorEnvironment
parameter, which is of the type
IProcessExtensionConfigurationEditorEnvironment,
you can create text
fields that support ivyScript and have smart buttons that provide access
to the process data, environment functions and Java classes.
Here is an example on how an editor could look like:
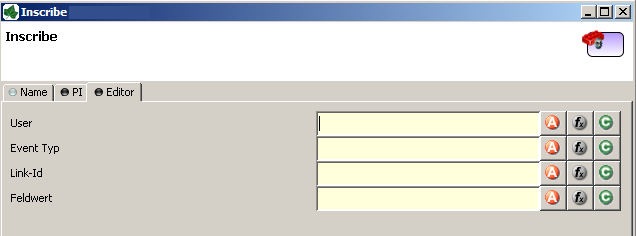
As you can see, the editor provides access to any process relevant data that can be used by your own process elements. For instance, you can easily transfer process data to your legacy system.
The following part shows the implementation of the above editor. As
mentioned earlier Axon.ivy provides the
IIvyScriptEditor that
represents a text field with ivyScript support and smart buttons. Inside
createEditorPanelContent use the method createIvyScriptEditor
from the editorEnvironment parameter to create an instance of such
an editor. Use the loadUiDataFromConfiguration method to read the
bean configuration and show within the UI components. Inside this method
you can use the methods getBeanConfiguration or
getBeanConfigurationProperty to read the bean configuration. Use the
method saveUiDataToConfiguration to save the data in the UI
components to the bean configuration. Inside this method you can use
methods setBeanConfiguration or setBeanConfigurationProperty to
save the bean configuration.
public static class Editor extends AbstractProcessExtensionConfigurationEditor
{
private IIvyScriptEditor editorUser;
private IIvyScriptEditor editorEventTyp;
private IIvyScriptEditor editorLinkId;
private IIvyScriptEditor editorFieldValue;
@Override
protected void createEditorPanelContent(Container editorPanel,
IProcessExtensionConfigurationEditorEnvironment editorEnvironment)
{
editorPanel.setLayout(new GridLayout(4, 2));
editorUser = editorEnvironment.createIvyScriptEditor(null, null, "String");
editorEventTyp = editorEnvironment.createIvyScriptEditor(null, null, "String");
editorLinkId = editorEnvironment.createIvyScriptEditor(null, null, "String");
editorFieldValue = editorEnvironment.createIvyScriptEditor(null, null);
editorPanel.add(new JLabel("User"));
editorPanel.add(editorUser.getComponent());
editorPanel.add(new JLabel("Event Typ"));
editorPanel.add(editorEventTyp.getComponent());
editorPanel.add(new JLabel("Link-Id"));
editorPanel.add(editorLinkId.getComponent());
editorPanel.add(new JLabel("Feldwert"));
editorPanel.add(editorFieldValue.getComponent());
}
@Override
protected void loadUiDataFromConfiguration()
{
editorUser.setText(getBeanConfigurationProperty("User"));
editorEventTyp.setText(getBeanConfigurationProperty("EventTyp"));
editorLinkId.setText(getBeanConfigurationProperty("LinkId"));
editorFieldValue.setText(getBeanConfigurationProperty("Feldwert"));
}
@Override
protected boolean saveUiDataToConfiguration()
{
setBeanConfigurationProperty("User", editorUser.getText());
setBeanConfigurationProperty("EventTyp", editorEventTyp.getText());
setBeanConfigurationProperty("LinkId", editorLinkId.getText());
setBeanConfigurationProperty("Feldwert", editorFieldValue.getText());
return true;
}
}
At runtime you have to evaluate the IvyScript the user have entered into
the ivy script editors. If you implement for example the
AbstractUserProcessExtension
class there is a perform method which
is executed at runtime. At this point you want to access the configured
data in the editor. The following code snippet show how you can evaluate
the value of an IIvyScriptEditor.
If you use the
IIvyScriptEditor you only get the value by calling the
executeIvyScript method of the AbstractUserProcessExtension.
public CompositeObject perform(IRequestId requestId, CompositeObject in,
IIvyScriptContext context) throws Exception
{
IIvyScriptContext ownContext;
CompositeObject out;
out = in.clone();
ownContext = createOwnContext(context);
String eventtyp = "";
String linkId = "";
String fieldValue = "";
String user= "";
user = (String)executeIvyScript(ownContext, getConfigurationProperty("User"));
eventtyp = (String)executeIvyScript(ownContext, getConfigurationProperty("Event Typ"));
linkId = (String)executeIvyScript(ownContext, getConfigurationProperty("Link-Id"));
fieldValue = (String)executeIvyScript(ownContext, getConfigurationProperty("Feldwert"));
// add your call here
return out;
}
Task Tab
On this tab you configure the task which is created when this element is executed by the awaitet event. This task will not appear in any user task list and is exclusively handled by the system. The values on this tab are therefore only relevant for analysing the finished tasks and not for the task list itself.
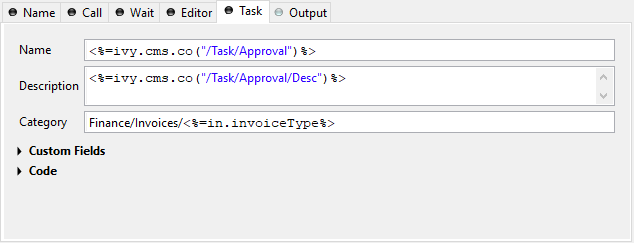
- Custom fields
The values set on this table are only informational and have no effect on how this task is treated by Axon.ivy. See Custom Fields.
- Code
This is a post construct code block for the Task that is defined in this tab. The created Task is provided as variable called
task. See Code.
Output Tab
On Output Tab you can configure the output of the element (i.e. the data that leaves the element).
Note
For each incoming connection you have a separate inX object
available which carries the data of the Xth input. Hover with the
mouse over the incoming connections of the element to learn which
input connection corresponds to which variable.