HTML content in the CMS
There are a number of specific content object types that are uniquely used inside HTML Dialog pages. All of them have their own editors, the usage of which is described in the following sections.
Note
Web Pages can be accessed without starting a process. This allows you to create for example a translated start page with some process start links. See also chapter Access CMS Content with a Browser.
Web Page Editor
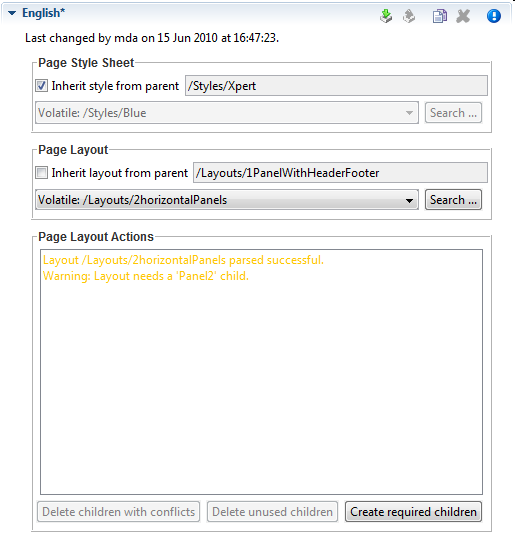
The Page Editor is used to specify the Style Sheet and Layout of a page. They can either be inherited from their parent objects in the CMS hierarchy or can be set explicitly. Use the combo boxes to set one of the style sheets, i.e. page layouts which are contained in the corresponding CMS top level folders. The Search… buttons on the other hand opens a dialog which does show all CSS and Layout content objects in the whole CMS to select one. So the children content objects of the page represent the selected Layout (see Layout Editor). The missing or obsolete parts (i.e. children in the CMS hierarchy) of a page (e.g. after changing layout) may be created or deleted with the corresponding buttons at the bottom of the editor.
HTML Panel Editor
This is the most important editor to edit your HTML content. Each Web Page (see Web Page Editor) has sections that are called Panels and which are defined by the page’s layout. Generally, a page has as many panels as are specified by its associated layout (see Layout Editor).
In the panels of a page, the actual content of the page is defined. Each content part of a panel is stored as an own content object below that panel’s content object inside the content management:
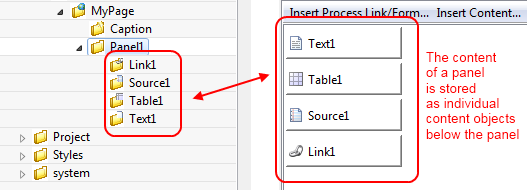
The contents of a panel are arranged in a table from left to right and from top-to bottom in a structured manner. Each table cell contains a single content object or some custom HTML or JSP code.
A panel can be rendered as plain HTML or as a HTML table. If it is
rendered with plain HTML cells are simply rendered one after another.
Rows are separated with a <br> tag. On the other hand, if it is
rendered as a HTML table, each cell will be rendered as a cell of the
table. You can switch the rendering kind using the checkbox As HTML
Table. Switching the rendering influences the available context menu
items of a cell and the buttons Table, Row and Cell.
You can switch between the Edit and the Source View of a panel. The Edit View as explained above shows the table of the panel with its cells. The Source View on the other hand shows the JSP Code that is generated from the Edit View.
HTML Table Editor
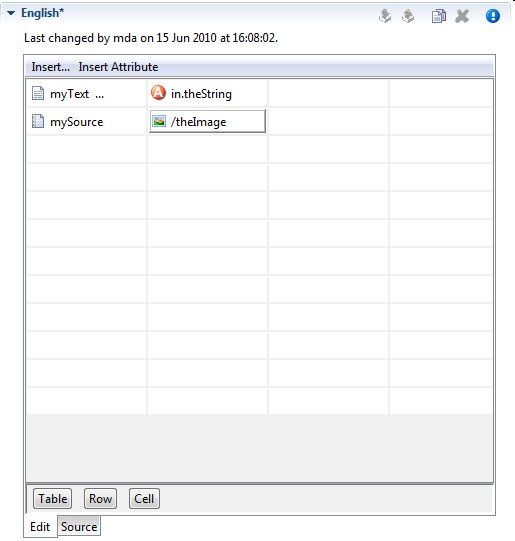
The HTML Table editor can be used to configure a HTML table. In contrary to the Result Table Editor the numbers of rows and columns is defined here statically. And for each cell the content must be chosen specifically although the content itself may be generated dynamically at run-time. Using the menu Insert… it is possible to use Text, Source or CMS elements and using the menu Insert Attribute it is possible to use attributes from the process data in the cell content.
Tip
A Text element can be inserted in a cell by just selecting the cell and starting to type the text. The Text Editor opens automatically then.
With the buttons Table, Row and Cell or the corresponding entries in the popup menu the HTML attributes for the corresponding table part can be manipulated. Furthermore you can add/delete table rows and merge or split table cells to influence the layout of the table. The source tab allows to view and edit the generated HTML code directly.
Typically a table object is not created as an independent content object in the CMS tree, but rather inserted below a Page content object. The cell contents are no first-class CMS elements but are stored within the HTML table content object itself.
Result Table Editor
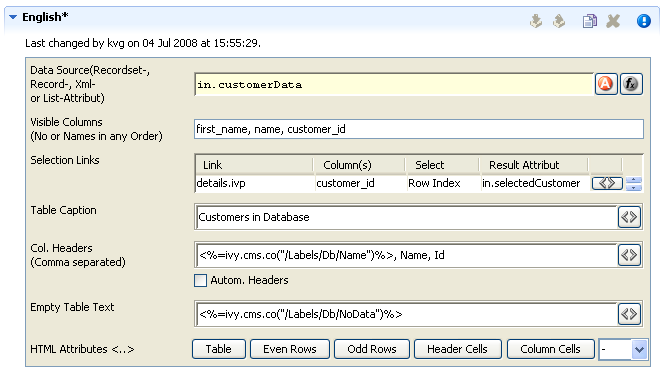
The Result Table editor is used to configure the dynamic generation of (HTML) data tables on either DB page or Page process elements. Typically a result table object is not created as an independent content object in the CMS tree, but rather inserted below a Page content object when a table gets inserted onto one of the pages panels (using the HTML Panel Editor).
- Data Source
Specify here the source of the result table’s data. You can select a recordset or a list as data source from the process data attributes.
- Visible Columns
Select the columns that should be rendered by the result table. You can either use the column numbers (1,5,8,2,3) or column names (name, first_name, customer_id) in a comma-separated list to specify subset and order.
- Selection Links
Hers it is possible to select which column entries that should be turned into a link for the one of the page’s output links. The select entry specifies what value that should be assigned to which result value (a process attribute). This is used to identify the selected record on the next process element.
- Table Caption
A caption text for the rendered result table. Macros may be used.
- Column Headers
Specify the names of the columns as they should appear in the header row as a comma-separated list. Macros may be used, the order must be the same as specified in the Visible Columns field.
- Automatic Headers
If selected, then the column headers will be selected from the specification in the database.
- Empty Table Text
The text to display if the source data is empty. May contain macros.
- HTML Attributes
Specify the HTML attribute values for table, even rows, odd rows, header cells and column cells.
For almost all of the above described features, the attributes of the corresponding HTML tags can be edited explicitly by clicking on the HTML tag button.
HTML Link Editor
Link editor is used to render process and static links. Whereas the execution of a process link will lead to the continuation of the process (i.e. activate a specific arc in the process model) and the activation of a static link leads to some other HTML page independent of the process.
Links can be rendered in many different forms, e.g. both the “classical” hyperlink as well as the display of a form with a submit button are considered to be special forms of links.
All of those different link types are configured with the HTML Link Editor. The link editor can be opened in two different ways: either by selecting a link content object below a page in the CMS editor tree or by double clicking on a link field in the HTML Panel Editor.
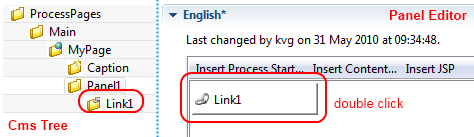
The following options can be configured for all links:
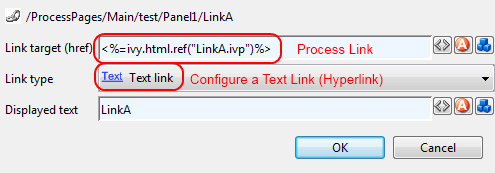
- Link Target (Href)
Specify the target of the link that will be jumped when the link is activated. If this is the configuration of a process link, then a macro that specifies the link that should be executed will already be specified (see example image above). However, any valid HTTP-link is accepted as value for this field, e.g.
http://www.acme.com.- Link Type
Specifies the visual appearance (type) of link that should be configured. Depending on the type that is selected, the configuration fields below this attribute will change.
Depending on the selected Link Type, additional options are available for configuration.
Configuring a Form Link
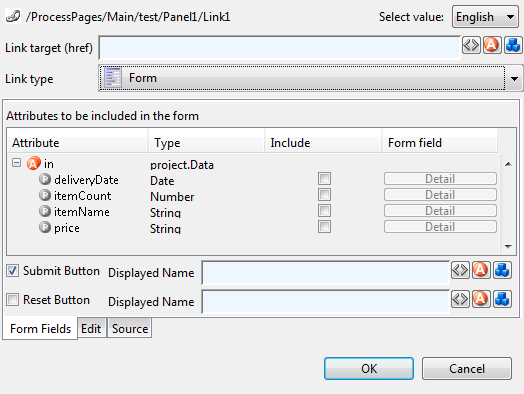
When selecting Form as Link Type the link editor will show a sub-editor that allows you to specify a form and all form fields, that are initialized and/or set from/to process data. Furthermore, you can configure whether a Submit and/or a Reset button should be displayed (including the text of the buttons). At the bottom you even have the choice to change the editor’s view for either designing the tabular layout of the form in a graphical editor or directly editing the HTML code.
At run-time the form defined in the Form Field Editor will be rendered in a HTML page. Clicking the submit button results in the continuation of the process of this element. Therefore, if you disable the submit button you have to ensure that a process link for process continuation is part of the HTML page (e.g. by adding such a link in the HTML view of the editor).
Configuring Form Field Details
If the Details button of a form field is clicked (when configuring a Form Link) a specialized sub-editor is presented to the user. This editor allows to configure in detail how a specific form field is to be rendered in HTML.
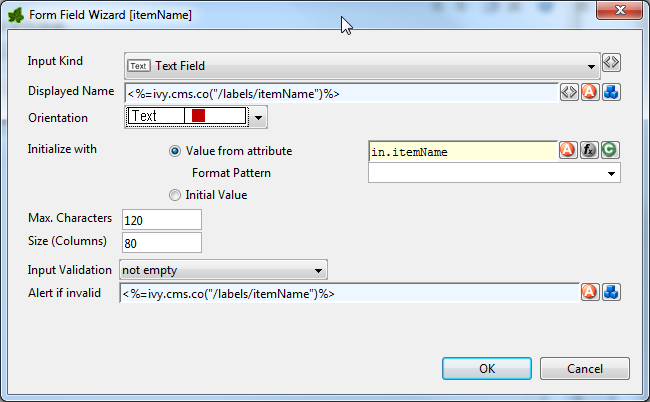
Several types of input kinds for the form fields are available such as text fields, lists or date pickers. For each type, the configuration and therefore the layout of this editor may differ slightly and some parts (irrelevant to the chosen) may be invisible. For most form fields you can define the layout, the default value and the validation.
- Input Kind
All the different input kinds Input Kind
Image
Description
HTML Tag
Text Field

A single line input field for text of all kind.
<input type="text">Password Field

The same as the text field but each inserted character is displayed as black bullet.
<input type="password" >Text Area

This is a multi line input field for text of all kind.
<textarea>Check Box

A simple box to selecting zero, one or more of two or more options (ideally for yes/no or true/false information). The data that is associated with the chosen option is saved.
<input type="checkbox" >Radio Button
It is sort of a button for selecting one and only one of two or more options which are mutually exclusive. The data that is associated with the chosen option is saved.
<input type="radio">Combo Box
A text field with an attached drop-down list to select from several predefined values.
<select size="0">List

A list to choose from several predefined values.
<select size="*nbOfOpti ons*">File Upload

With this input kind, the user can choose a file to upload to the Axon.ivy Engine file area
<input type="file">Hidden Field

Hidden fields can be used to transfer additional data invisible for the user (for use in e.g. JavaScript or e-mail transfer of forms)
<input type="hidden">Date Picker

To choose a date. Note that the date is displayed according to the language set in the browser of the user (while simulating in the Designer you can set the language in the toolbar). Note too, that if dates are entered in a 2-digit format, then Axon.ivy will interpret numbers within the next 20 years as years in the future. All other numbers are interpreted as years from the past (e.g. in 2010 entering 30 leads to 2030 whereas entering 35 leads to 1935). The Javascripts used for the Date Picker are copied into the webContent folder of the project to scripts/datepicker and scripts/jquery.
Implemented in Java Script
- Displayed Name
Axon.ivy adds a text label to the form field for reference. The text of this label can be set here using process data or CMS entries.
- Orientation
It is possible to choose how the label and the form field are positioned to each other, either side by side or super-imposed.
- Initialize with…
You can use process data, function return values (both value from attribute) or plain text (initial value) to set a default value for the form field. For check boxes it is additionally possible to select whether it is checked or not.
Warning
Make sure that the data types of the default value matches to the chosen form field otherwise an error will be thrown at runtime.
- Maximum Characters
The maximum number of characters which are allowed to enter. The user will not be able to enter more characters.
- Size (Columns)
You can set the width of the form field to layout your forms nicely.
- Options
Here the content of the list based form fields (Combo Box, List, Check Box, Radio Button) can be defined. You can either choose an Ivy Script Recordset or List (select options form attribute) or you can define the content in a table with values and display texts. For recordset based content, the first column is used as values and the second column as display texts (all other columns are omitted). For list based content all the list entries are used as value and as display names.
- Values per Row
For check boxes and radio buttons it is possible to define how many options are rendered in the same line (or row)
- Rows
Only used for the list form field. It represents the number of visible rows in the list. If more items than rows are defined, the list will have scroll bars.
- Mime Type
Is only used for the file upload form field. The mime type corresponding to the type of file which can be uploaded.
- Input Validation
By selecting an input validation script you may validate the values that an user enters in a specific field on the client, e.g. before the form is submitted. If the user tries to submit a form but input validation fails on some of the form fields, then a message will be displayed to the user and the form will not be sent.
Axon.ivy offers you a number of built in validation functions that can be selected from the Input Validation combo box. The scripts that are available depend on the input kind of the currently edited form field (e.g. different scripts are available for checkbox and text input fields).
If the built-in scripts do not satisfy your needs, you may provide your own validation scripts written in JavaScript. Read the section How to provide own HTML Validation Scripts to learn more about this topic.
Warning
Please note, that JavaScript must be enabled in your client’s browsers in order for the validation scripts to work!
- Alert message if invalid
For any selected Input Validation a predefined warning message exists. If you don’t like the default message, you may specify a custom message that will be displayed if the entered value is invalid.
You may use the content smart button to select and insert a textual content object that should be displayed as message or as part of your message. This allows you to specify messages in multiple languages.
If you leave the field empty, the default message of the selected validation script will be displayed.
Smart Table Content Editor
On the Smart Table Content editor you configure what content to show in the smart table. You can configure the data source for the table. Furthermore, you can influence the visual look and feel and set options such as header, body or footer label texts, for each entry in the table.
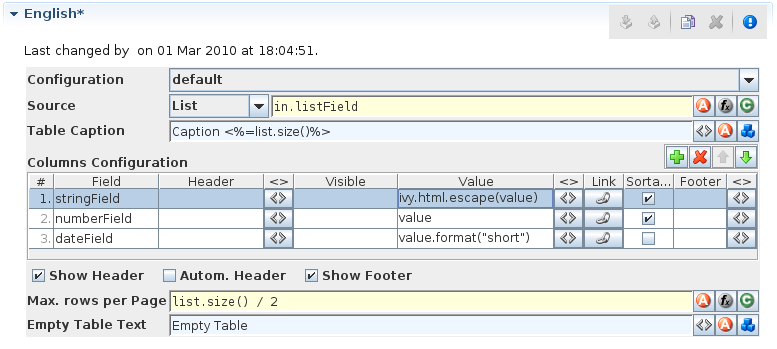
Smart Table Content Editor
Accessibility
Content Management -> Smart Table Content Object
Features
- Configuration
Select the Renderer Configuration which is used when the Smart Table is rendered and then displayed on the client browser. See the Smart Table Configuration Editor for more details.
- Source
Select the type of the source for your table. Either
List,RecordsetorRecord. Define in the IvyScript text field the path to your source.- Table Caption
Enter a text to display as caption of the table. Use IvyScript macros if needed. example:
<%=ivy.cms.co("/labels/header")%>- Columns Configuration:
- Columns (a column configuration is shown as row in the editor)
Field: Define the name of the field of your data source to map to the current column. If your data source is a list, then the list elements must contain a field or method with the configured name (e.g.userNameorgetUserName()). If your data source is a recordset, then the records must have a field with the configured name. The value of the field is mapped to the variablevaluewhich you can use in the IvyScript text field of theValuefield.Header: Enter a text to display as header of the column. Use IvyScript macros if needed, e.g.<%=ivy.cms.co("/labels/header")%>. Note hat this has only an effect if theShow Headercheck box is selected too.Visible: Enter a IvyScript expression which results in a Boolean value, to configure the visibility of the column. If no condition is set, then the column is visible.Value: Enter a IvyScript expression to configure what label that should be displayed in the table cell. This IvyScript is executed for every cell in this column (once per row in the table).Link: Choose the link where the process goes if we click on a cell on this column. It is also possible to define the process attributes where to store the row index, the column index or the column name.Sortable: Activate this check box if you want your table to be sortable. Clicking on the header of a column triggers then a sorting of the whole table according to the selected column. The variablevalueis used for sorting which is defined in the columnField.Footer: Enter a IvyScript expression to configure what label that should be displayed in the table footer.<>: Allowed to edit the HTML attributes for the table header, body or footer cells. E.g. choose colors or borders. Note that this specific settings of HTML attributes will override any settings from the configuration.- Actions
Add: Adds a new column configuration to your table definition. The column configuration will be shown as row in the Columns Configuration table.Remove: Removes the selected Column Configuration(s) from your Columns Configuration table.Up: Moves the selected Columns Configuration(s) up in the table. This means that the column(s) moves one position to the left in the resulting table.Down: Moves the selected Columns Configuration(s) down in the table. This means that the column(s) moves one position to the right in the resulting table.Show Header: Activate this check box if you want your table to have a header row.Autom. Header: Activate this check box if you want the system to label your headers.Show Footer: Activate this check box if you want your table to have a footer row.- Variables
in: The process data at the point of time when this CMS element is executed.index: Table index of the currently selected table entry.originalIndex: Index of the currently selected entry in the data source (without respect to the visual order, e.g. after a sorting).value: The value of the currently selected field (as defined in the field column) in the data source element (i.e. record).it: The currently rendered element of this widget’s list data source (only available, if the source is of type List).list: The list defined as data source (only available, if the source is of type List).record: The currently selected record (only available, if the source is of type Recordset).recordset: The recordset defined as data source (only available, if the source is of type Recordset).
- Max. rows per Page
Enter a IvyScript expression to configure the maximum number of rows are shown per page.
- Empty Table Text
Enter a plain text that will be displayed if the table source is empty.
JSP Editor
The JSP editor is used to edit a JSP content object which can be used in the Web Page, Process End Page, Task Switch Event or Task Switch Gateway process elements.
Inside JSP content objects you can make use of the Environment Variable ivy. It is imported and declared as follows:
<%@ page import="ch.ivyteam.ivy.page.engine.jsp.IvyJSP"%>
<jsp:useBean id="ivy" class="ch.ivyteam.ivy.page.engine.jsp.IvyJSP" scope="session"/>
You can also use the in object (i.e. process data) of the process
where the associated process element is located. You can access the
process data by using the ivy.html.get() method, e.g.:
<%=ivy.cms.co("myUri")"%>
<%=ivy.html.get("in.myString")%>
Furthermore you can insert references to content from the web content directory into your JSP content objects, e.g.:
<jsp:include page="/jspToInclude/include.jsp" />
<img src="images/myImage.jpg" >
Layout Editor
The Layout editor is used to edit a JSP Layout content object which defines the Layout of an HTML dialog page (see Web Page Editor).
Inside the Layout JSP content objects you can make use of the Environment Variable ivy or you can insert references to content from the web content directory (see JSP Editor).
For the layout creator there are some useful functions on the ivy variable:
Layout functions |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Returns the URL to the CSS style, which is set on the current HTML Editor). |
|
The layout creator can define a placeholder for content, that the page designer should fill in. When a page with this layout is created the specified placeholder is created as a content object with the given name and type under the HTML dialog page whose value is set by the page designer. At execution time the value of the content object is set as a String into the layout. |
|
This creates a Panel content object with the specified name under the HTML dialog page when a page with this layout is created. |
A very simple JSP Layout example which includes the style of the page, creates a content object named Caption with the type String and a Panel content object with the name Panel1 looks as follows:
1<%@ page import="ch.ivyteam.ivy.page.engine.jsp.IvyJSP"%>
2<jsp:useBean id="ivy" class="ch.ivyteam.ivy.page.engine.jsp.IvyJSP" scope="session"/>
3<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
4<html>
5 <head>
6 <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="<%=ivy.style()%>"/>
7 <title><%=ivy.content("Caption","String")%></title>
8 </head>
9 <body>
10 <jsp:include page='<%=ivy.panel("Panel1")%>' flush="true"/>
11 </body>
12</html>
Link Browser
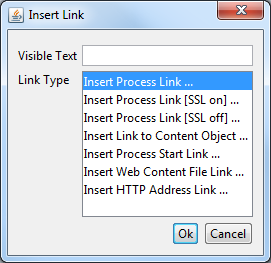
The link browser can be used to insert a HTML <a href="..."> link
tag. The appearing dialog shows the available link types to choose from.
If you select a link type and then press Ok (or double-click the
link type), then another dialog appears to configure the link.
- Visible Text
The visible text of the HTML link that will be inserted. Or, in HTML language, the text between the
<a>and the</a>tags.- Link Type
The type of link to insert.
Link Type |
Description |
HTML href link target |
|---|---|---|
Process |
A link to continue the process with the corresponding sequence flow out of the Web Page element that shows this page. The link target is addressed relatively, i.e. uses the same protocol like the request to the page. See the section for the inscription mask of the web page element for further information about process links. |
|
Process (SSL on) |
Same as the process link, but addresses the process link absolutely using HTTPS. |
|
Process (SSL off) |
Same as the process link, but addresses the process link absolutely using HTTP. |
|
Content Object |
This is a link to a content object in the CMS. Note that not all content object types may be used but only the ones that represent file-based resources. This holds true especially for file-based content objects such as images or documents. |
|
Process Start |
A link that starts a new process. Note that the process is started in a new case. |
|
Web Content |
For linking to a resource in the web content folder. |
|
HTTP Address |
Inserts a link to an arbitrary web resource such as a web page or a video on the web. |
|
Other content editors
Content editors that are not described in this chapter are described in the Content Object Value Editors chapter.